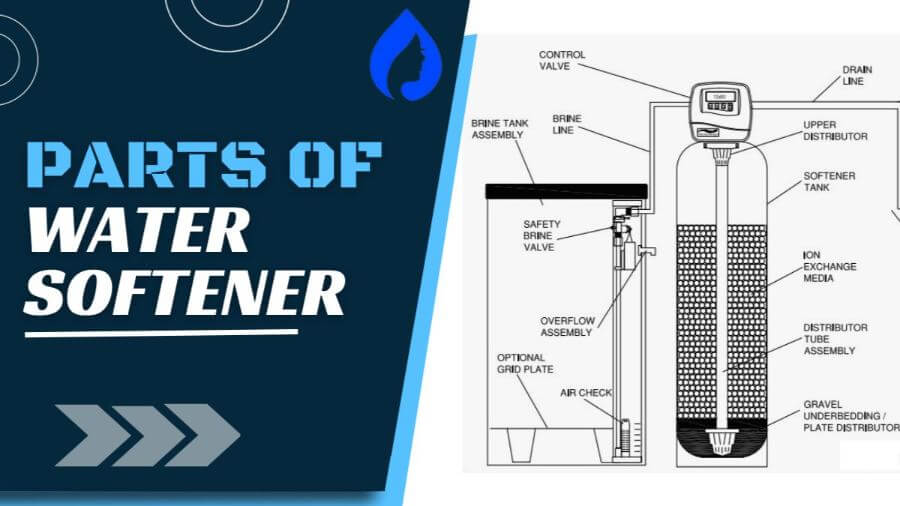
A salt-based water softener contains 3 primary components for softening water:
Some other necessary parts include:
Follow along to explore how different parts of a water softener work to make your water soft and nice!
🎯What Are The Parts of a Water Softener System?
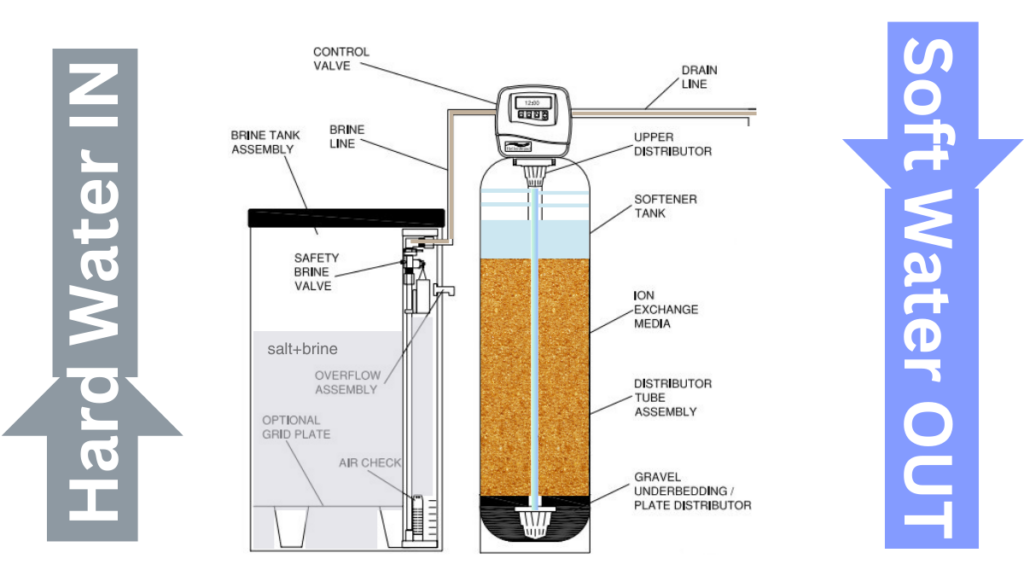
Here are the three main parts of a water softener:
⚙ A Resin Tank (Mineral Tank)

The primary function of the water softener, which is to soften water, occurs in a resin or mineral tank.
The resin tank contains negatively charged resin beads, making a bed of resin.
When water flows through the resin tank, these beads attract positively charged hard water minerals like calcium and magnesium and exchange them with sodium ions, resulting in softened water.
A periodic regeneration replenishes the capacity of the resin beads and clears all the stuck hard water minerals.
The mineral tank connects with the control head, which regulates the water flow and performs the regenerative task when scheduled.
Also Read: 5 Ways To Remove Sodium From Softened Water
🧂A Brine Tank (Salt Tank)

The brine tank is a shorter tank with brine for regeneration, mostly sodium or potassium chloride.
Brine, during the regeneration process, moves to the mineral tank for rinsing and recharging the resin beads.
This brine then works to flush out the calcium or magnesium minerals from the resins.
Like the resin tank, the brine tank also connects to the control head, helping it deliver the brine solution to the mineral tank when needed.
⚙️Control valve or head valve
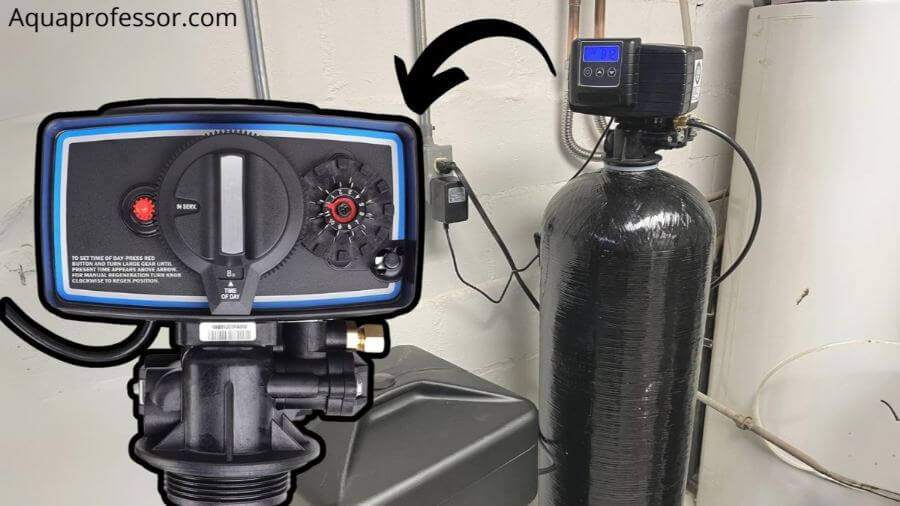

A control valve is like the water softener’s brain. It regulates the flow of water and the frequency of the regeneration cycle and initiates REGEN.
Modern water softeners can monitor and measure various factors like regular water use, hard mineral content in the water, and the capacity of the mineral tank.
According to these factors, it decides the regeneration cycle frequency and schedules it for a particular time.
The control valve is a central link between the resin tank, mineral tank, and water supply.
Some other common water softener parts of a standard salt-based system include:
Besides the above parts, two additional components of water softeners are:
Also Read: 7 Types Of Water Softeners
🤔What Are The Workings Of A Water Softener?
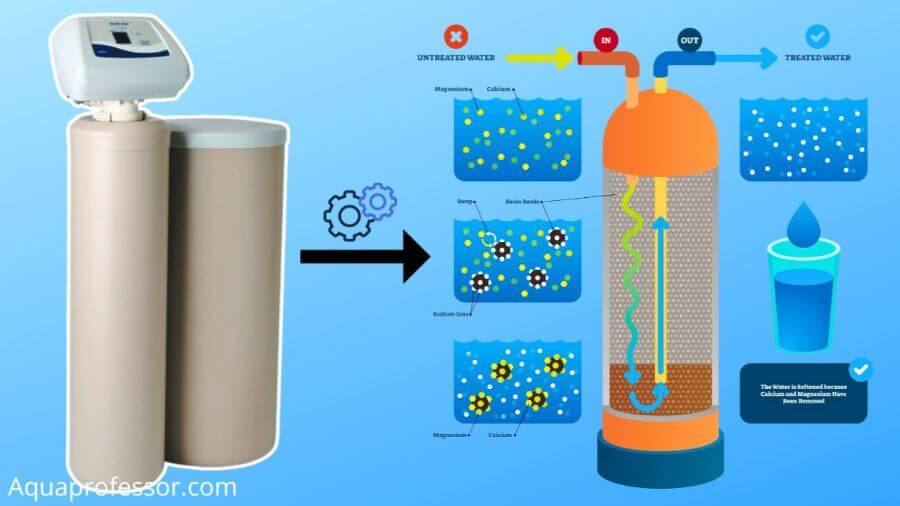
The salt-based water softeners use an ion-exchange method to convert hard water to soft water. Here’s what happens in a water softener:
💡Parts Of A Water Softener: FAQs
What are the two tanks on a water softener?
The two tanks on a water softener are the resin tank and the brine tank.
The resin tank contains beads of negatively charged resins for water-softening by following the ion exchange process.
The brine tank stores sodium or potassium salts, which form a solution of salt, which is helpful during the regeneration cycle and recharges the ion exchange capacity of those plastic beads.
Can I replace the resin in my water softener?
Yes, you can replace the resin in your water softener. Here’s the step-by-step process:
1. Check out the user manual to determine your resin tank size and how much resin you need. Purchase quality resin beads and other essentials from your manufacturer or online.
2. Bypass the water supply and set the REGEN to manual mode. Afterward, turn off the power supply to the water softener.
3. Remove the control head and start picking up all the resin beads and dumping them. Rinse the tank afterwards.
4. Carefully cut and install the new riser tube. Then, add the resin beads, following the instructions in the manual.
5. Rescrew the control head and refill the water softener. Next, turn the bypass valve to its normal position and turn on the power outlet.
Is water softener resin dangerous?
No, water softener resin isn’t dangerous as it is composed of non-toxic plastic materials.
However, old, degraded resins can leach away and dissolve in water through excessive chlorine exposure or lack of proper maintenance, elevating the risk of contamination.
Can a water softener tank be repaired?
Yes, you can repair a water softener tank with minor damage. Follow the steps to fix the issues yourself:
1. Find the root cause by inspecting each section of the water softener tank.
2. Clean the brine tank of impurities and salt crusts.
3. Run iron-out of the resin tank to capture all the trapped irons.
4. Clear the sediments from the resin tank injector.
5. Check for minor leaks caused by loose seals and repair them with a new seal or patch.
Moreover, use good-quality salt and perform regular maintenance to avoid damage as much as possible.
How often do you add salt to a water softener?
You should add salt to your water softener every 6–8 weeks. However, it depends on water hardness, daily water consumption, and the frequency of REGEN.
Set phone reminders and keep an extra stock of salt to avoid your water softener running out of salt.
Sayan understands that access to clean water doesn’t have to be costly.
He strives to provide knowledge of water purification techniques in the simplest way possible so that we can lead a healthy life without breaking our bank.
