
Yes, if you’re using city water, you may require a water softener, especially if your city water is hard, like Marion, Iowa, Phoenix, Arizona, and Las Vegas, Nevada.
I know it sounds contrary to popular belief, but hear me out:
Municipal authorities often remove excess iron and manganese but not the ones causing hardness, like calcium or sodium ions, as they’re not considered a health risk.
So, if you’re a resident of these areas, a water softener can be beneficial if you don’t want spotty dishes or clogged pipelines.
Continue reading for an in-depth guide on using water softeners with city water.
👀Do Cities Have Hard or Soft Water?
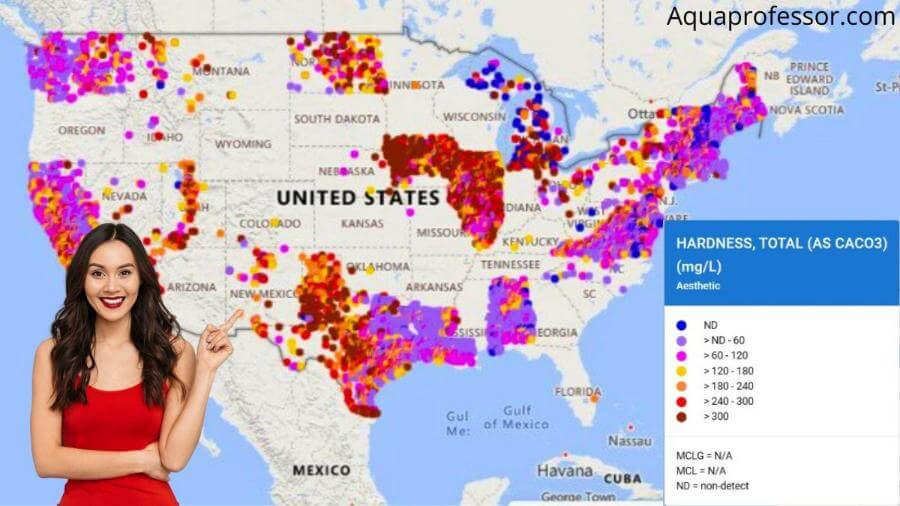
According to the U.S. Geological Survey, approximately 85% of the U.S. has hard water. It includes cities like Indianapolis, Las Vegas, and Phoenix.
Most city authorities, such as Prior Lake and Chanhassen do not treat water for hardness. There are four main reasons:
However, this doesn’t mean all cities don’t treat hard water. For example, the City of Ann Arbor in Michigan treats its water to reduce hardness. Therefore, it’s possible to have soft-treated city water, especially if you live in a region with soft water naturally or your city treats water for hardness.
It’s best to check with your local water authority or consult the municipal water quality reports to verify if your city’s water supply undergoes water treatment for hard water. Obviously, you can pay attention to tell-tale signs to point out water hardness.
🚰What Are Signs That You Have Hard Water?
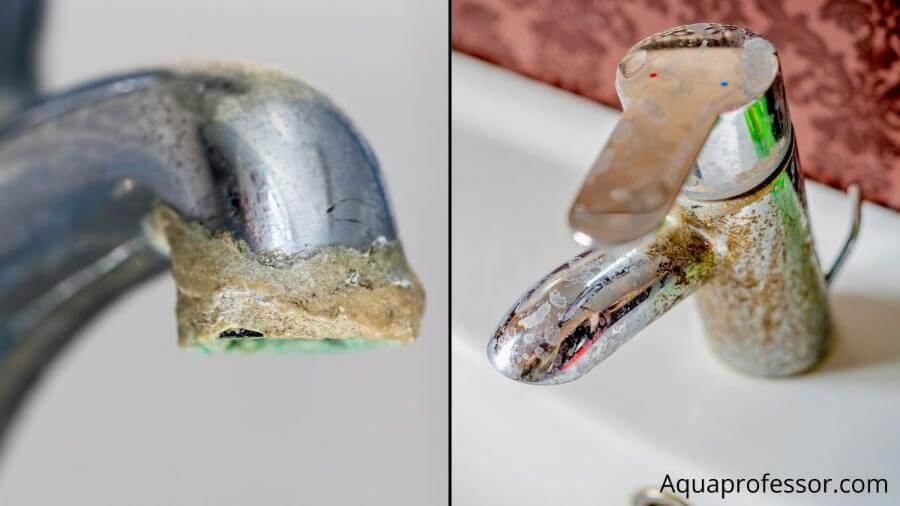

Here are some common signs that you may have hard water in your home:
🤔Do You Need a Water Softener if You Have Hard Water?
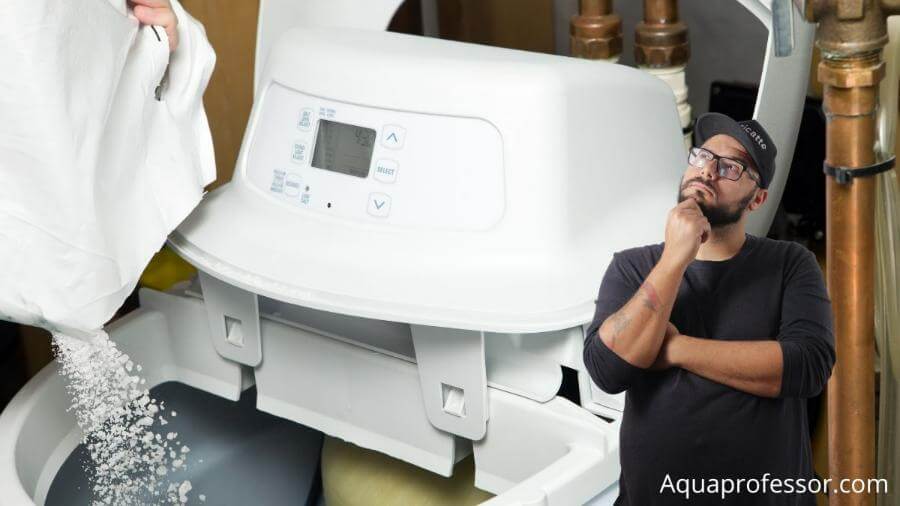

Yes, if you have hard water, a water-softening system can benefit your home.
Water softeners, particularly salt-based ones, use an ion exchange process to soften water and prevent the problems associated with hard water. They can even remove up to 1 ppm of iron from your water.
However, it’s crucial to consider the environmental impact of water softeners. Some states have banned salt-based water softeners due to their environmental footprint, which includes increased salt in wastewater that can harm aquatic life.
A water conditioner could be more environmentally friendly if your water has low to medium hardness (less than 120 mg/L).
How do water conditioners work?
Water conditioners work by reducing scale buildup rather than removing the healthy minerals that cause hardness. It can be particularly useful if you’re using city water, which typically contains a different level of sediments, contaminants, and minerals than well water.
It’s best to evaluate your water’s hardness and the problems it might be causing before deciding on a water treatment solution.
❓Do I Need A Water Softener With City Water: FAQs
What happens if you don’t use a water softener?
Without a water softener, hard water can cause limescale buildup or soap scum in your plumbing system and appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan.
Do you need a water softener for well water?
Private well water often contains high levels of minerals like magnesium, calcium, and other minerals, which cause hardness, so a water softener can be beneficial in preventing problems associated with hard water.
What is the downside of a water softener?
While water softeners can be beneficial in treating hard water, there are also potential downsides of water softening systems that you should consider:
High Sodium Content – Water softeners often use salt to remove calcium and magnesium in hard water. This process can add sodium ions to your drinking water, which may not be suitable for people on a low-sodium diet.
Costly to Install and Maintain – Water softeners can be expensive to install, and they require regular maintenance and replenishment of salt, which can add to their overall cost.
Not Environmentally Friendly – If discharged carelessly, water softener backwash can end up in bodies of water and soil, affecting plant and animal life.
Should you drink tap water if you have a water softener?
While it’s generally safe to drink softened water, it can increase the sodium content in your drinking water. It might not be suitable for people on a low-sodium diet or those with high blood pressure.
How do you reduce water hardness without a softener?
There are several ways you can reduce water hardness without using a water softener system:
Boiling: This method is especially effective for temporary hardness caused by calcium and magnesium bicarbonates. The heat converts these bicarbonates into insoluble carbonates, which can then be removed from the water.
Vinegar or Lemon Juice: This method can be particularly useful when washing your hair or cleaning the dishes.
Chelating Agents: Substances like citric acid can bind with hard minerals, keeping them soluble and preventing them from causing hardness.
Adarsh is a Health & Nutrition Sciences graduate with expertise in environmental health. He is associated with ventures like Glacier Fresh Filter and Simpure Filter Systems. Through Aqua Professor, he intends to provide helpful information to every home to help them make smarter decisions.
